Introduction:
Chest cancer, often referring to lung cancer, is a critical health concern worldwide. With rising cases and mortality rates, understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options is essential for early detection and improved outcomes.
Table of Contents
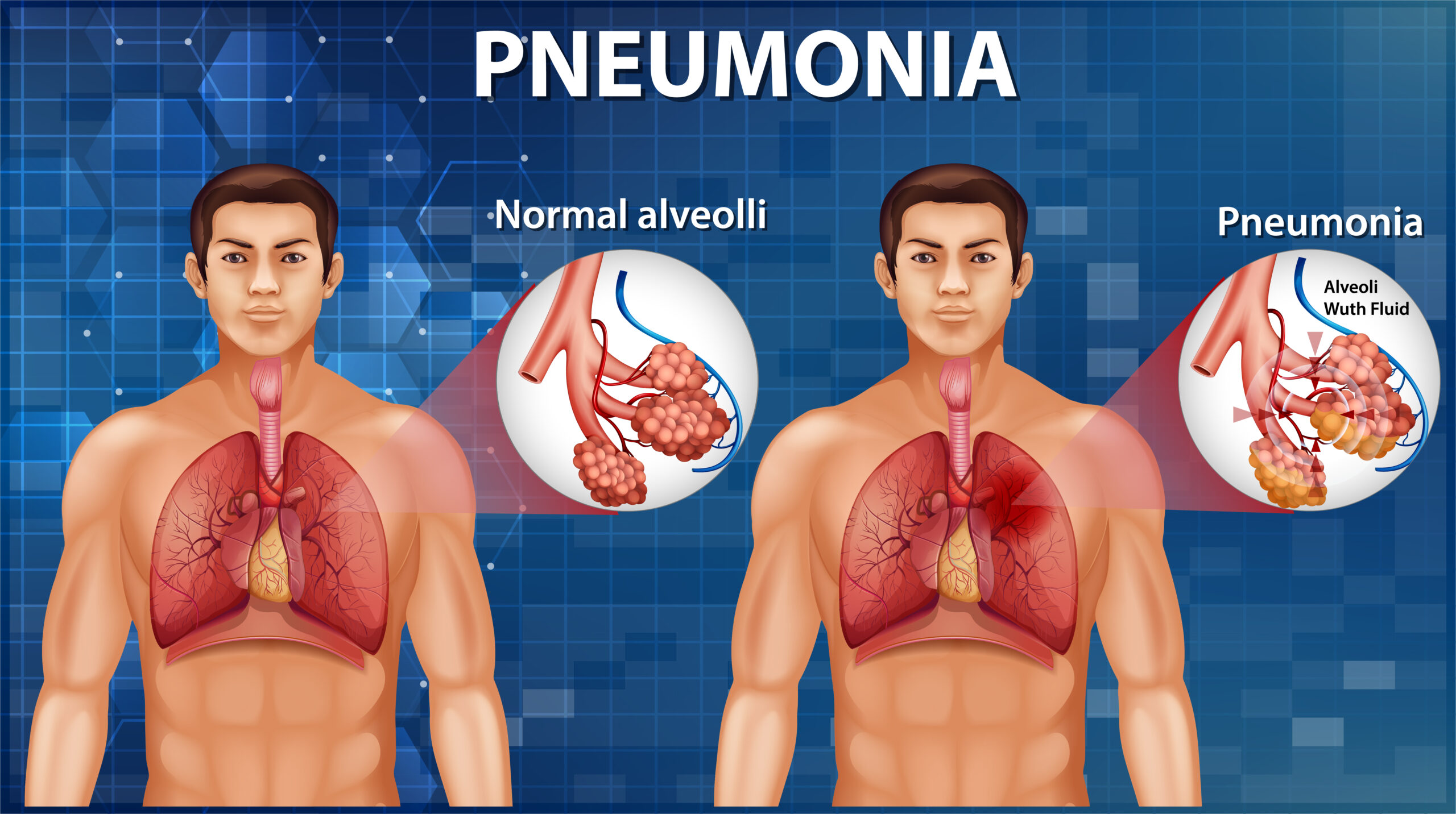
What is Chest Cancer?
Chest cancer primarily encompasses lung cancer, which develops in the lungs and may spread to other parts of the body. It can be classified into two main types:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This is the most common type, accounting for about 85% of cases.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This type is less common but tends to grow more rapidly.
Symptoms of Chest Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of chest cancer is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough that worsens over time
- Chest pain that may be constant or worsen with deep breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Recurrent respiratory infections
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of chest cancer is not fully understood, several risk factors contribute to its development:
- Smoking: The leading cause of lung cancer, responsible for approximately 85% of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure increases risk, even for non-smokers.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to asbestos, radon gas, and other carcinogens can elevate risk.
- Family History: Genetics may play a role, especially if close relatives have had lung cancer.
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly for individuals over 65.
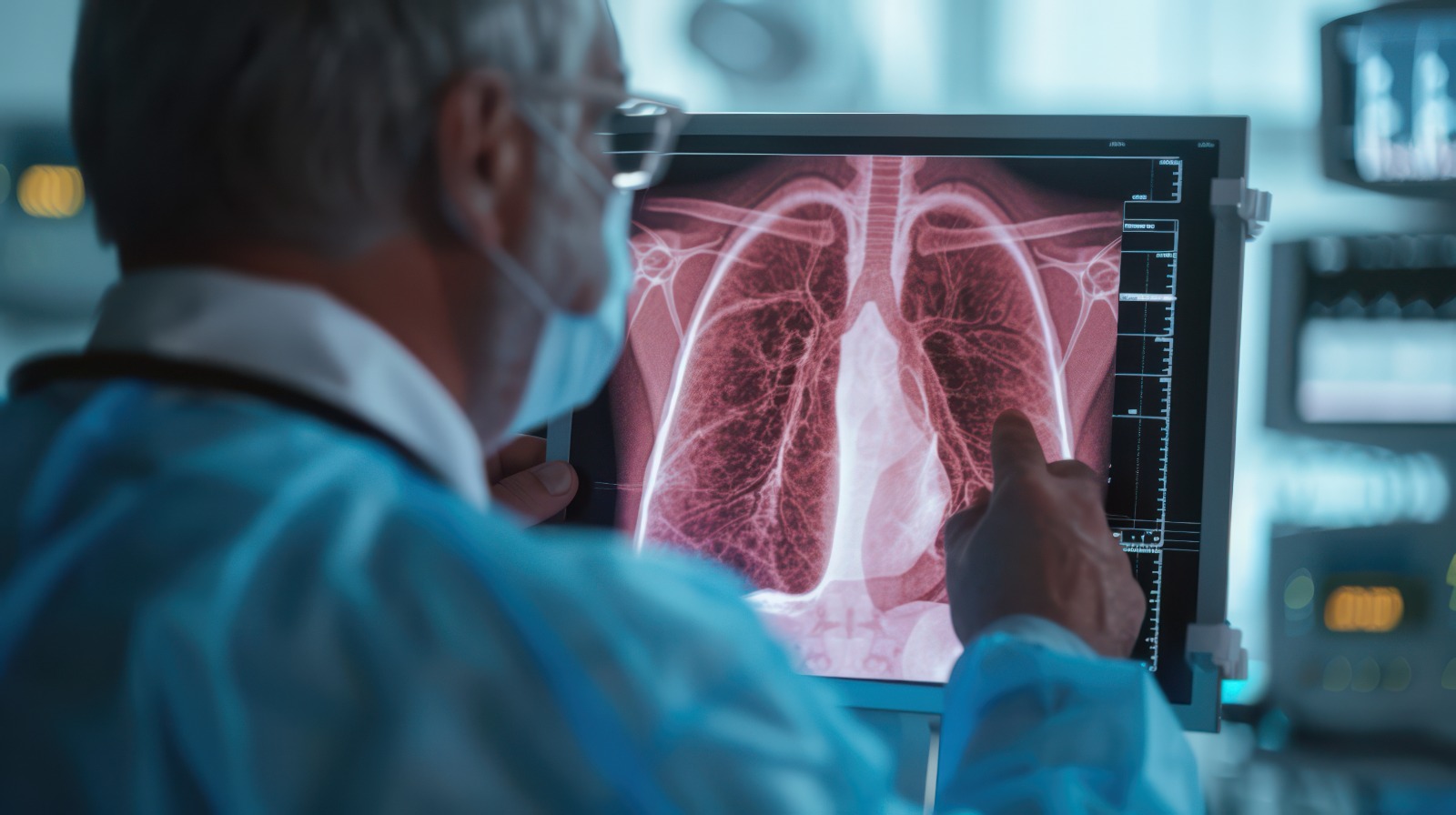
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is vital for effective treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help identify tumors.
- Biopsy: A sample of lung tissue is analyzed for cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: May help assess overall health and detect markers.
Treatment Options
Treatment for chest cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Options include:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue, if feasible.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic treatment with drugs to target cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific characteristics of cancer cells, offering a more personalized approach.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases can be prevented, several strategies can reduce the risk of developing chest cancer:
- Quit Smoking: Seek support and resources to stop smoking.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Maintain smoke-free environments.
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection through screenings, especially for high-risk individuals.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Chest cancer is a serious health issue, but early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments is essential for everyone, especially those at risk.
FOR MORE:https://international-health-fitness.com/understanding-substance-abuse-a-growing-global-concern/
cancerhttps://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3986-breast-cancer
FAQS:
What are the main symptoms of chest cancer?
Who is at risk for developing chest cancer?
How is chest cancer diagnosed?
What treatments are available for chest cancer?
Can chest cancer be prevented?




Chest cancer is a serious health issue, but early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments is essential for everyone, especially those at risk.