Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer globally, significantly affecting millions of lives each year. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of lung cancer, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Table of Contents
What is Lung Cancer?
Tumors are formed when aberrant cells in the lungs grow out of control, leading to lung cancer. There are mostly two kinds:
1-Approximately 85% of instances of lung cancer are of the most prevalent kind, known as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and giant cell carcinoma are among its subtypes.
2-Although less frequent, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is more aggressive in its nature. It frequently spreads swiftly to other bodily regions.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The following variables may raise one’s risk of lung cancer:
1-About 85% of cases of lung cancer are caused by smoking, which is also the main cause of the disease.
2-Secondhand Smoke: Lung cancer can also result from being around someone else’s smoke.
3-Environmental Exposure: Extended exposure to other carcinogens, asbestos, or radon gas may raise the risk.
4-Family history: Having a history of lung cancer in one’s family may increase your risk.
5-Age: Risk rises with advancing years, particularly for individuals over 65.
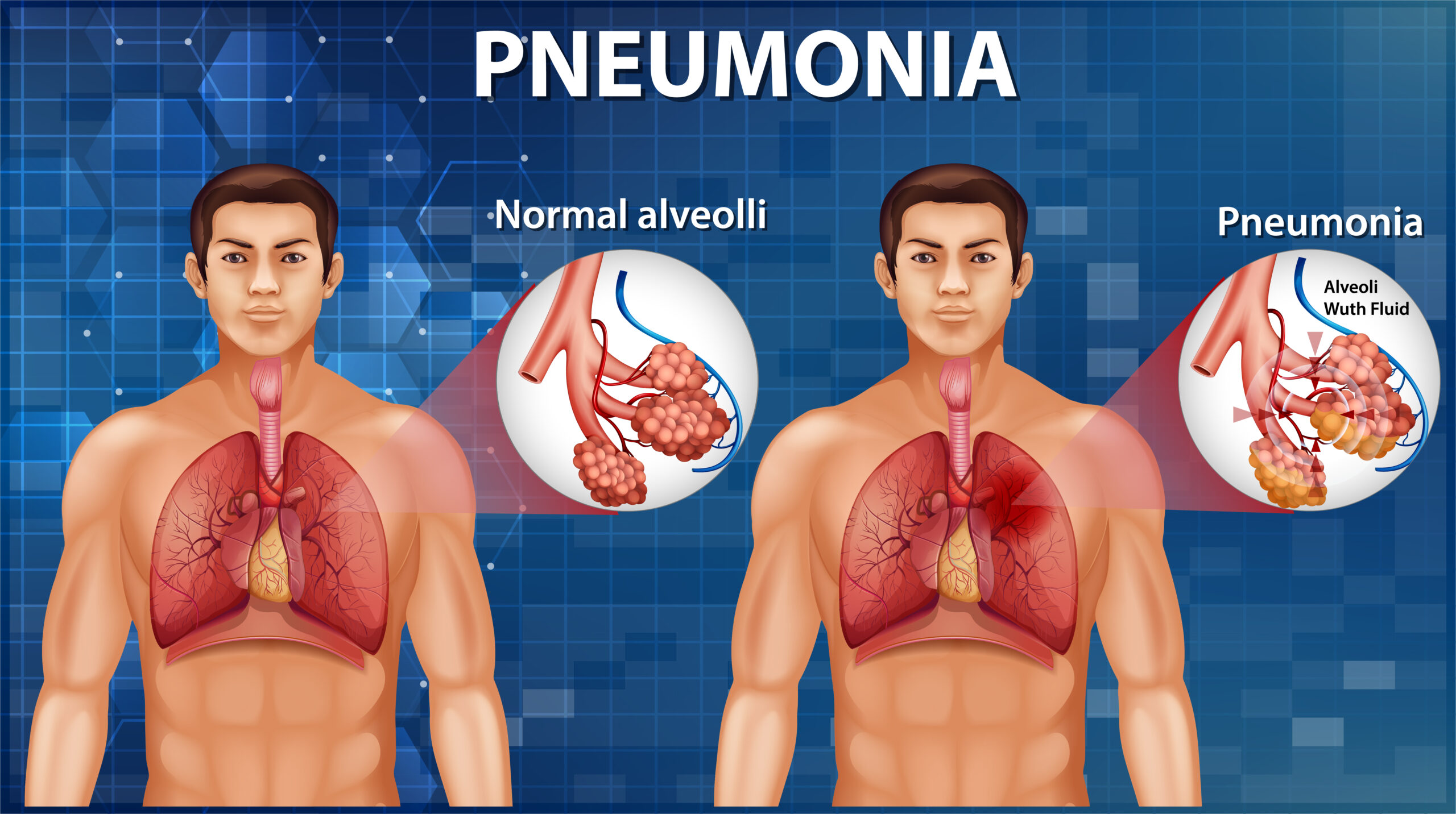
Symptoms of Lung Cancer:
Early-stage lung cancer may not present noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Diagnosis:
If lung cancer is suspected, a healthcare provider may conduct several tests, including:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans to visualize the lungs.
- Sputum Cytology: Examining mucus for cancer cells.
- Biopsy: Removing a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis.
- Molecular Testing: Identifying specific mutations in cancer cells to guide treatment.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor and surrounding tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy waves to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Employing drugs to destroy cancer cells or stop their growth.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention:
While not all lung cancer cases can be prevented, certain measures can significantly reduce risk:
- Quit Smoking: Seek help and resources to quit smoking.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Minimize exposure to environments where smoking is prevalent.
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding environmental toxins can help.
FAQS:
What are the survival rates for lung cancer?
Can lung cancer be cured?
What should I do if I experience symptoms?
Is lung cancer only caused by smoking?
How can I support a loved one with lung cancer?
Conclusion:
Understanding lung cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. By recognizing risk factors and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards their health. Remember, consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options is essential. If you have concerns about lung cancer, do not hesitate to reach out for support and information.




Thank you for this informative blog! Your insights on lung cancer awareness are incredibly valuable. Understanding the symptoms and risk factors can truly make a difference. Keep up the great work!