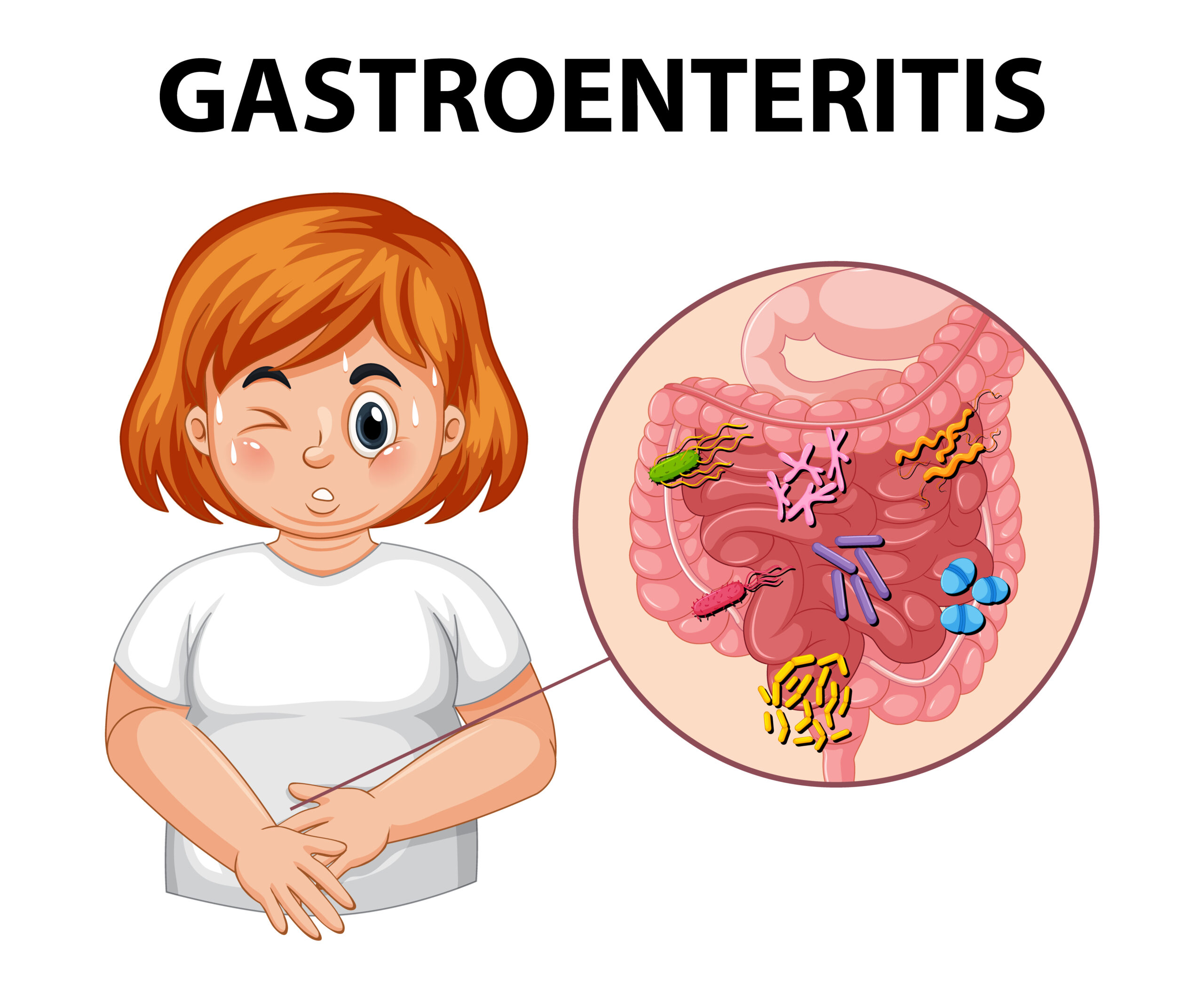
The “stomach flu,” or gastroenteritis, is an inflammation of the intestines and stomach. Although bacterial infections, parasites, and specific drugs can also cause this illness, viral infections are the most common cause. An extensive examination of gastroenteritis, including symptoms, treatments, and preventative strategies, is given in this article.
Table of Contents
What is Gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis is characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. The condition can be acute or chronic, with acute gastroenteritis being the most common form.
Causes of Gastroenteritis:
1-Viral Infections: The most common viruses that cause viral infections are rotavirus and norovirus. Food, water, or contaminated surfaces can all spread these infections. They can spread quickly.
2-Bacterial Infections: When contaminated food or water is consumed, bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Campylobacter can frequently cause gastroenteritis.
3-Parasitic Infections: Two parasites that can induce gastroenteritis are Giardia and Cryptosporidium. They are usually caused by water that is tainted.
4-chemicals and medications: A wide range of chemicals and medications have the potential to irritate the gastrointestinal tract and produce symptoms that resemble gastroenteritis.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis:
Although they can vary, gastroenteritis symptoms usually include:
1-Diarrhea: Watery, frequent stools.
2-Vomiting is the result of abrupt, intense nausea.
3-Abdominal Pain: Constriction or unease in the lower abdomen.
4-Swelling of the body temperature.
5-Muscle aches and headaches are frequent in viral episodes.
6-Dehydration: signs and symptoms include lightheadedness, reduced urine, and dry mouth.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis: A healthcare provider typically diagnoses gastroenteritis based on medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. In some cases, stool samples or blood tests may be required to identify the causative agent.
Treatment:
1-Hydration: Preventing dehydration is the main course of treatment. Make sure you consume enough of fluids, such as clear broths, ORS, or water. Steer clear of alcoholic or caffeinated beverages as these can exacerbate dehydration.
2-Rest: Getting enough sleep is essential for healing. Get lots of sleep so that your body has time to recuperate.
3-Diet: Reintroduce simple-to-digest meals, such as bread, applesauce, rice, and bananas, gradually (the BRAT diet). Until you fully recover, stay away from dairy products, fatty foods, and spicy foods.
4-Medication: Over-the-counter anti-diarrhea products could be beneficial, but before using them, speak with a doctor. Only after a bacterial infection has been identified are antibiotics recommended.
5-Preventing Contagion: In the event that a virus is the source of the gastroenteritis, take precautions to keep others from getting sick. Always wash your hands, and refrain from preparing food for others.
What to Do and What to Avoid:
What to Do:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink fluids regularly to replace lost electrolytes.
- Rest Well: Ensure you get enough sleep to help your body recover.
- Eat Lightly: Follow a bland diet initially and gradually return to normal eating.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly, especially after using the bathroom and before eating.
What to Avoid:
*Prevent Dehydration: Relying just on alcoholic or caffeinated drinks can make you more dehydrated.
Steer clear of solid foods.
*First: Avoid solid foods until the vomiting stops and the frequency of diarrhea decreases.
*Steer clear of dairy products because they might exacerbate symptoms and be difficult to digest when recovering.
*Avoid Close Contact: To stop the sickness from spreading if the infection is viral, stay away from people in close proximity.
Prevention:
Preventing gastroenteritis involves several key practices:
- Practice Good Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the bathroom.
- Ensure Safe Food Handling: Cook meats thoroughly, wash fruits and vegetables, and avoid consuming unpasteurized dairy products.
- Drink Safe Water: Use clean, safe drinking water and avoid consuming water from unreliable sources.
Conclusion:
The common but treatable illness known as gastroenteritis is characterized by intestinal and stomach irritation. If the problem develops, you can treat it appropriately by being aware of its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Maintaining proper cleanliness, handling food safely, and consuming clean water are all important ways to prevent gastroenteritis. Recall to drink plenty of water, get plenty of rest, and if you’re impacted, gradually resume eating.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or persistent, or if you think you may be dehydrated. You can lessen the negative effects of gastroenteritis on your health by adopting these preventive steps and using the right treatment plans.
MORE ARTICLES:https://international-health-fitness.com/simple-strategies-for-managing-chronic-pain/
FAQS:
What is gastroenteritis?
How is gastroenteritis spread?
What are the common symptoms of gastroenteritis?
How can I prevent gastroenteritis?
When should I see a doctor for gastroenteritis?




One thought on “Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Health Tips4”